Regular verbs are an important part of language, and luckily, they’re relatively easy to learn. So, now we’ve seen a regular verbs definition, let’s break it down and find out the exact meaning of regular verbs and how they operate. We can also look at some regular verbs examples so you can see them in action.
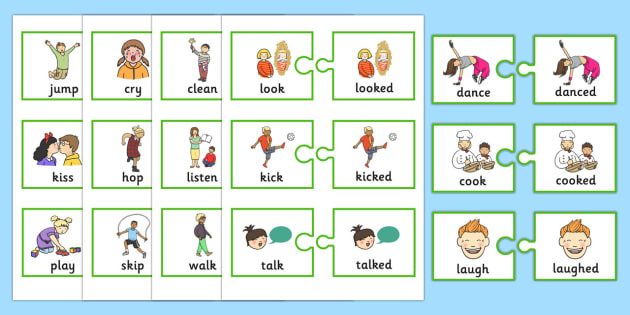
We all use regular verbs every day, but we probably don’t even notice them. In fact, there are two in that sentence - “use” and “notice” are both examples of regular verbs. This is because they can be transformed into the past tense simply by adding “-ed” or “-d” to the end of the verb, like this:
So, a regular verb always takes this very predictable form when we’re moving it from the present into the simple past tense.
Some more regular verbs examples include:
It’d be useful to reference some of these verb examples, or come up with more of your own, when teaching children about them. Often, a grammatical concept such as verbs benefit from a working example so that children can see how it works in practice.
You can do this with the help of resources, too! Something like this Using Verbs Worksheet will help children further their understanding after reading through these verb examples.
As you can see, each of these verbs can very easily be turned into its past-tense equivalent. This is why regular verbs are the first ones children learn - they make it as easy as possible for children to talk and write about what has happened in the past.
There are thousands of regular verbs in English! Each of them behaves the same way as the regular verb examples we’ve given here. If you want to talk about something that’s already happened, you add “-ed” or “-d” to the end of the verb.
A participle is a non-finite verb that can also be used as an adjective. For example:
In the first sentence, the word “burned” is being used as an adjective. In the second, it is used as the past participle.
The past participle of a verb is always used with the verb “to have” (“He has burned his finger”). It is most often used to form the past perfect tense, to describe an action that has already been completed.
Here are some more examples of past participle regular verbs:
The great thing about regular verbs is that they don’t change their form at all between the simple past tense and the past participle. You still form them simply by adding “-ed” or “-d” to the end of the regular verb.
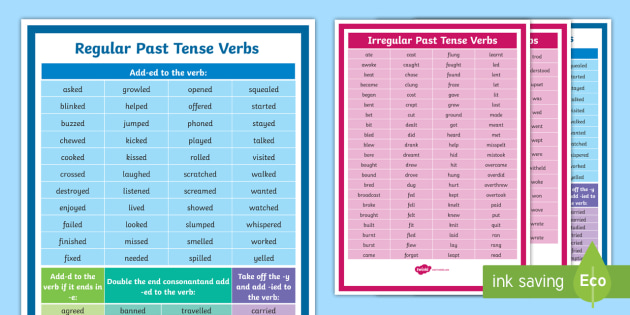
If a verb can’t be put into the past tense easily, if the verb doesn’t fit with the ending “-ed” or “-d”, or the verb needs to change its form to make sense in the past, this means it’s an irregular verb. These are more tricky to learn, because they don’t follow the regular pattern that you’d expect when you put them into the past tense. Some examples of irregular verbs include:
English is full of irregular verbs, and they each have to be learned on a case-by-case basis. Children are usually not taught irregular verbs until they have grasped how regular verbs work and feel confident using them.
We hope that this regular verbs meaning and examples page is helpful when it comes to teaching children about regular verbs and how to use them in the past tense. However, children learn in all kinds of different ways, and it helps if you have plenty of engaging resources to increase their understanding of the topic. Our experienced in-house teachers have put together a wide range of materials and activities you can use to help children learn all about regular verbs:
You can also find plenty more resources to help you teach the different types of verbs and how to use them here.